Clang_atoi 함수
기초부터 다지자는 마음에서 C언어 공부 중에 몰랐던 내용을 하나씩 추가해보고자 한다.
첫 시작은 atoi 함수
atoi
Input : char* , Output : int
Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char x[10] = "450";
int result = atoi(x);
printf("integer value of the string is %d\n", result);
char* str_ptr= "33500";
result = atoi(str_ptr);
printf("integer value of the string is %d\n", result);
str_ptr = "hello_world";
result = atoi(str_ptr);
printf("integer value of the string is %d\n", result);
return 0;
}
Result
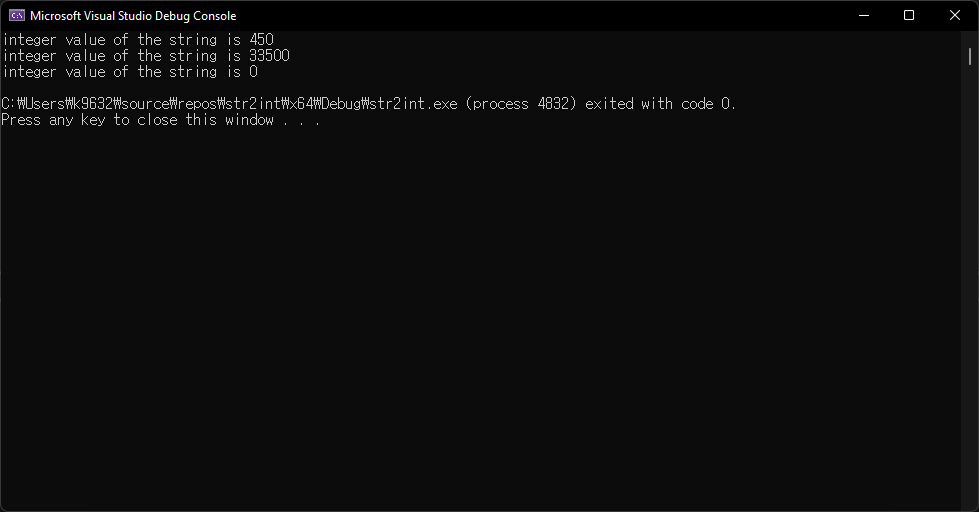
읽는 방법은 “에이투아이” 또는 “아토이” 등으로 사람마다 다른 듯 하다.
stdlib.h에 포함되어 있으며, 기본적으로 C언어의 문자열을 나타내는 char[n]을 int 타입으로 변경해준다.
입력은 위와 같이, 문자열을 받으며, 따라서, char[n] 또는 char*를 입력으로 받는다.
그리고 int로 변경한 후, 반환한다.
만약 입력으로 들어온 문자열이 정상적인 숫자가 아닐 경우, 0을 반환한다. (마지막 부분)
문제 풀이 중에, 입력으로 숫자를 여러 개를 입력 받는 경우가 있는데, 이와 같은 상황에서 유용하게 쓰일 것으로 보인다.